- Phone:+86 15218629499
- Phone: +86 15766990063
- E-mail: Yzprinting01@163.com
The rise of printed films marks a significant trend in packaging and branding. According to recent industry reports, the global printed films market is projected to reach $XX billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of XX%. This growth is driven by increasing demand in sectors like food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods.
Printed films serve various purposes. They enhance product visibility and provide essential information. Brands leverage printed films for effective marketing strategies. For example, vibrant graphics and clear labeling can influence consumer choices. However, the environmental impact of these materials is a concern. Many companies must balance aesthetics with sustainability.
Despite the advancements, challenges persist. The production process can produce waste, and recycling options remain limited. Innovating new materials that are both effective and eco-friendly is crucial. As industries seek to improve their practices, the role of printed films will continue to evolve. Understanding these dynamics is essential for stakeholders seeking growth and sustainability in a competitive landscape.
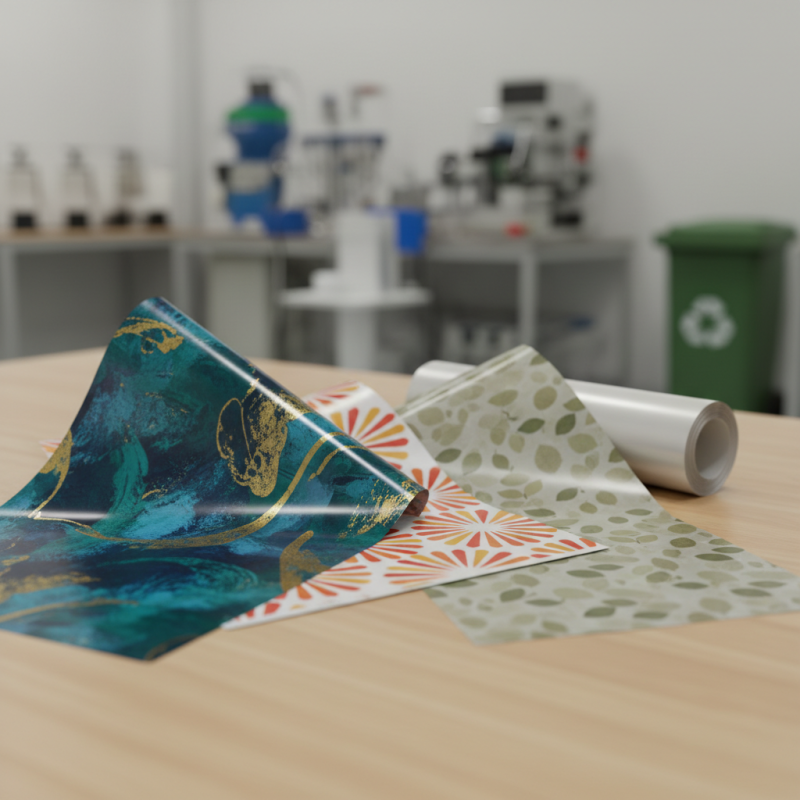
Printed films are versatile materials commonly used in various applications. They are typically thin layers of plastic that have been printed on with specific designs or information. These films can come in a range of finishes, such as matte or glossy. Their adaptability makes them suitable for packaging, labeling, and even decorative purposes.
One notable characteristic of printed films is their durability. They resist moisture and can withstand various environmental factors. This quality is essential for products that require long-lasting packaging. However, the process of printing on these films can be delicate. Ink adhesion may vary, leading to inconsistent results. Additionally, the choice of materials can impact the final product's effectiveness. Some films may not hold up well under stress, leading to potential issues down the line.
Another aspect to consider is the intended use of printed films. For instance, films used in food packaging must meet specific safety standards. This requirement complicates the production process and may lead to higher costs. It's essential to balance quality with affordability. While printed films can enhance a product's appeal, their benefits may not always justify the investment. Testing and feedback are crucial to achieve the desired outcome.
Printed films play a significant role in various industries. They are used for packaging, labels, and even electronics. In the food industry, for example, printed films are essential for maintaining freshness. According to a market report, the global flexible packaging market is expected to reach $300 billion by 2026. This highlights the critical role of printed films in ensuring product safety.
In the cosmetic sector, printed films provide eye-catching visuals on packaging. These films not only promote products but also protect them from damage. Additionally, the pharmaceutical industry relies on printed films for safe and compliant labeling. A recent study notes that 60% of pharmaceutical products use printed films for their packaging. This adherence to regulations ensures that consumers receive safe and effective medications.
Tips: When choosing printed films, consider their material properties. Not all films are suitable for every product. Test different types to see what works best. Always stay updated on industry trends. Innovations in materials can lead to better performance. It's crucial to ask, are your printed films environmentally friendly? This is an area where improvement is needed.
Printed films are versatile materials that play significant roles in our daily lives. These films come in various forms, such as labels, packaging, and promotional materials. According to a recent industry report, the global printed films market is projected to reach approximately $30 billion by 2025, highlighting their immense value.
In everyday settings, printed films are commonly seen in food packaging. For example, flexible films ensure freshness and extend shelf life. They provide a barrier against moisture and contaminants. A study showed that around 70% of all processed food products utilize printed films. This statistic reflects their importance in maintaining quality and safety. However, challenges persist in recyclability and sustainability of these materials, prompting businesses to explore eco-friendly alternatives.
In retail, printed films attract consumers' attention. Vibrant graphics and catchy slogans can influence purchasing decisions. One report indicated that products with eye-catching labels sell 30% more than others. Still, not all designs strike the right balance between aesthetics and information. Companies must reconsider how to convey messages effectively without overwhelming consumers. The future of printed films includes innovation and responsibility in usage.
| Application | Material Type | Usage Description | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food Packaging | Polyethylene (PE) | Used to seal and protect food items, extending shelf life. | Food & Beverage |
| Labeling | Vinyl | Applied to bottles and containers for branding and information. | Consumer Goods |
| Protective Films | Polypropylene (PP) | Used to shield surfaces from scratches during transport. | Electronics |
| Decorative Films | Polyester (PET) | Used in home decor items like window films and wallpapers. | Interior Design |
| Medical Applications | Medical-grade films | Used for bandages and other medical supplies for wound protection. | Healthcare |
The manufacturing process of printed films involves several key steps. It begins with material selection. Various substrates like plastic and paper are commonly used. These materials are chosen based on the end-use of the printed film. After selecting the substrate, the next step is preparing the design. This involves digital artwork and layout adjustments. The clarity of the design is crucial. Even small mistakes in design can lead to issues later.
Once the design is ready, the printing phase begins. Various printing techniques are employed, including flexographic and digital printing. Each technique has its own strengths and weaknesses. For instance, flexographic printing is efficient for large runs but may require longer setup times. On the other hand, digital printing offers flexibility for smaller batches. After printing, the films are often coated or laminated for added durability. This step can make a significant difference in the film's longevity and overall appearance.
Finishing touches are applied before the films are cut to size. Quality control is essential throughout this process. Any imperfections can affect the final product. Even minor issues, like color misalignment or surface texture, can lead to customer dissatisfaction. Thus, attention to detail is necessary for success in printed film manufacturing.
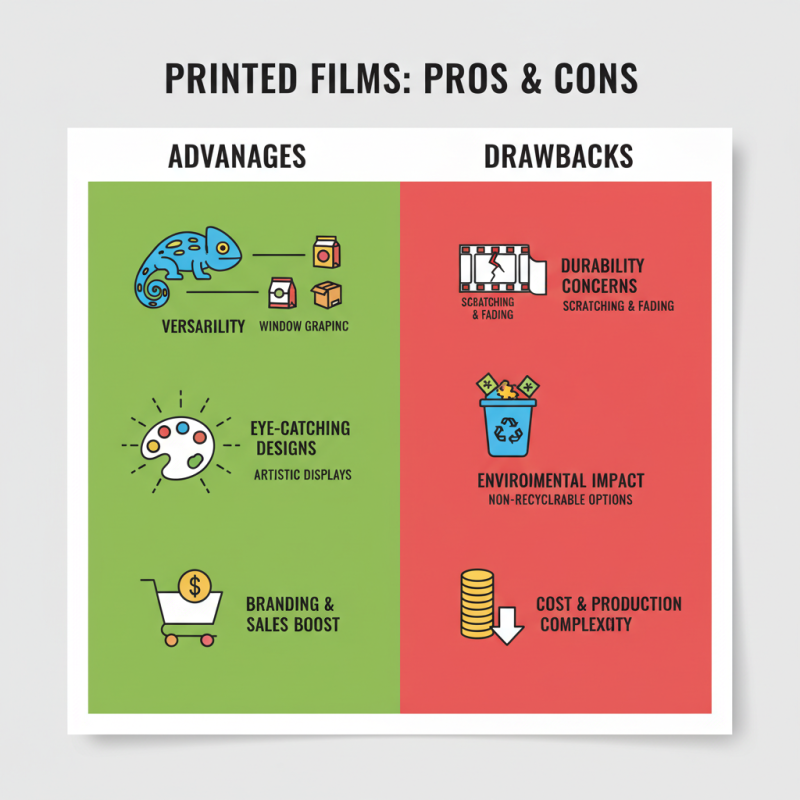
Printed films are widely used in various industries. They offer unique advantages, but some drawbacks can’t be ignored. One major advantage is their versatility. These films can be tailored for different applications, from packaging to artistic displays. Their vibrant colors and prints can catch attention and drive sales.
On the flip side, there are disadvantages to consider. The production process can be costly. High-quality printed films often require advanced technology and skilled labor. This can limit accessibility for smaller businesses. Moreover, printed films may not be as durable as other materials, especially when exposed to harsh environments. They can fade or tear, leading to increased waste.
Another important aspect is recycling. While some printed films are recyclable, many are not. This poses an environmental challenge. Consumers and manufacturers need to be aware of this issue. It's essential to weigh these pros and cons carefully before opting for printed films. Balancing quality, cost, and environmental impact is crucial for sustainable choices.






